Publications
Below is a selection of research papers I’ve authored during my time at SDU. These publications reflect my academic focus on game development and artificial intelligence.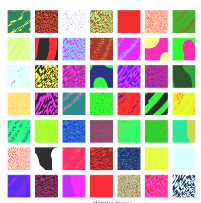
Towards Interactive Evolutionary Camouflage Design
IEEE Conference on Games (CoG), 2024
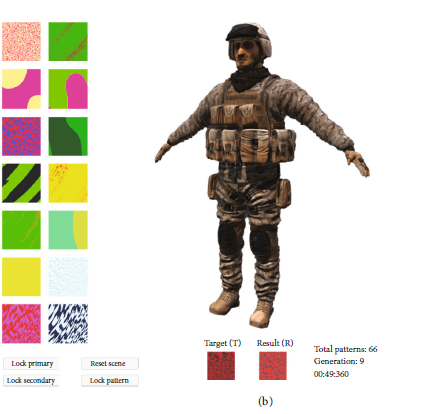
Abstact: This project presents an evolutionary algorithm for texture generation that allows users to choose and manipulate camouflage patterns. The initial results of a pilot study provide some insight into usability and the users’ ability to replicate a target pattern. The result is an evaluation of gathered data showing user tendencies and how they engage with the system. These tendencies include significantly different completion times for target patterns varying in complexity. Additionally, participants mostly agreed that the tool is helpful for future games and objects other than camouflage skins. The findings suggest potential applications for artificial intelligence in enhancing user customization and design flexibility. Further research must address technical limitations and explore broader game industry implications.
Evolving Camouflages: A User-Centric AI Approach for Game Aesthetics
International Journal of Computer Games Technology (2025)
Abstact: Artificial intelligence (AI) can create icons, skins, and camouflages for games. An optimal implementation of such a concept might provide new and more advanced features that benefit the user experience. This project investigates the use of an evolutionary algorithm for texture generation and allows users to choose and manipulate camouflage patterns. This enables users to create camouflage patterns that could theoretically be implemented in a video game. This study is supported by user testing to gather insight into usability and the users’ ability to replicate a target pattern. The result is an evaluation of gathered data showing user tendencies and how they engage with the system. These tendencies include significantly different completion times for target patterns varying in complexity. Additionally, participants mostly agreed that the tool is helpful for future games and objects other than camouflage skins. The findings suggest potential applications for AI in enhancing user customization and design flexibility. Further research is needed to address technical limitations and explore broader game industry implications. A brief introduction to the system described in this paper was published as a short paper in the IEEE Conference on Game (CoG) (Ploug et al. 2024).
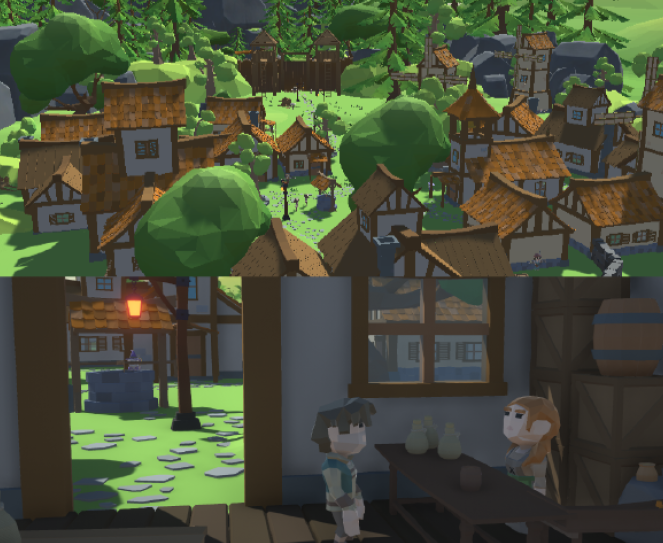

Open-Ended NPC Dialogue Favors Casual Players: A Pilot Comparison of Three LLM-Driven Dialogue Systems
IEEE Conference on Games (2025)
Abstact: Non-player character (NPC) dialogue plays a crucial role in shaping the player experience in narrative-driven video games, influencing agency, immersion and story engagement. Despite the recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) for dynamic dialogue generation, few empirical studies have compared their impact across different dialogue system designs. This pilot study explores how LLM-driven dialogue systems affect the player experience using a custom-developed role-playing game (RPG) featuring four different dialogue designs; static control (CV), rephrase (A), hybrid (B) and fully open-ended (C). Behavioral data and post-game questionnaires were collected from 64 participants. Results indicate that fully open-ended dialogues led to significantly longer dialogue interactions and higher overall engagement, particularly among casual players, with the survey feedback highlighting its immersive and natural tone. These findings suggest that fully open-ended LLM-based dialogue in video games can enhance narrative depth and player involvement. Index Terms—Large Language Models, NPC Dialogue, Casual Players, Player Engagement, Dialogue Systems, Procedural Narrative.
Open-Ended NPC Dialogue Favors Casual Players: A Pilot Comparison of Three LLMDriven Dialogue Systems
IEEE Conference on Games (2025)
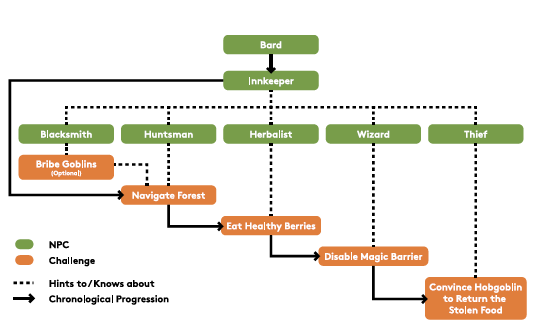
Abstact: QUEST OF AIVENGARDE is a custom-built roleplaying game (RPG) that features a traditional dialogue tree alongside three alternative systems, each incorporating large language models (LLMs) to varying degrees — ranging from rephrasing to fully open-ended conversations. The systems are embedded in a shared game world with consistent narrative and challenges, allowing direct comparison of their design trade-offs. The prototype is intended as a modular testbed for future research, offering a flexible framework to experiment with dialogue models in controlled, interactive settings.